A Thought Experiment
The thought experiment below better illustrates the interaction between (3) and (2) shown in Renewable Energy; The Sheppard Fractor
The Sheppard factor - Theoretical magnetic monopole
Where:
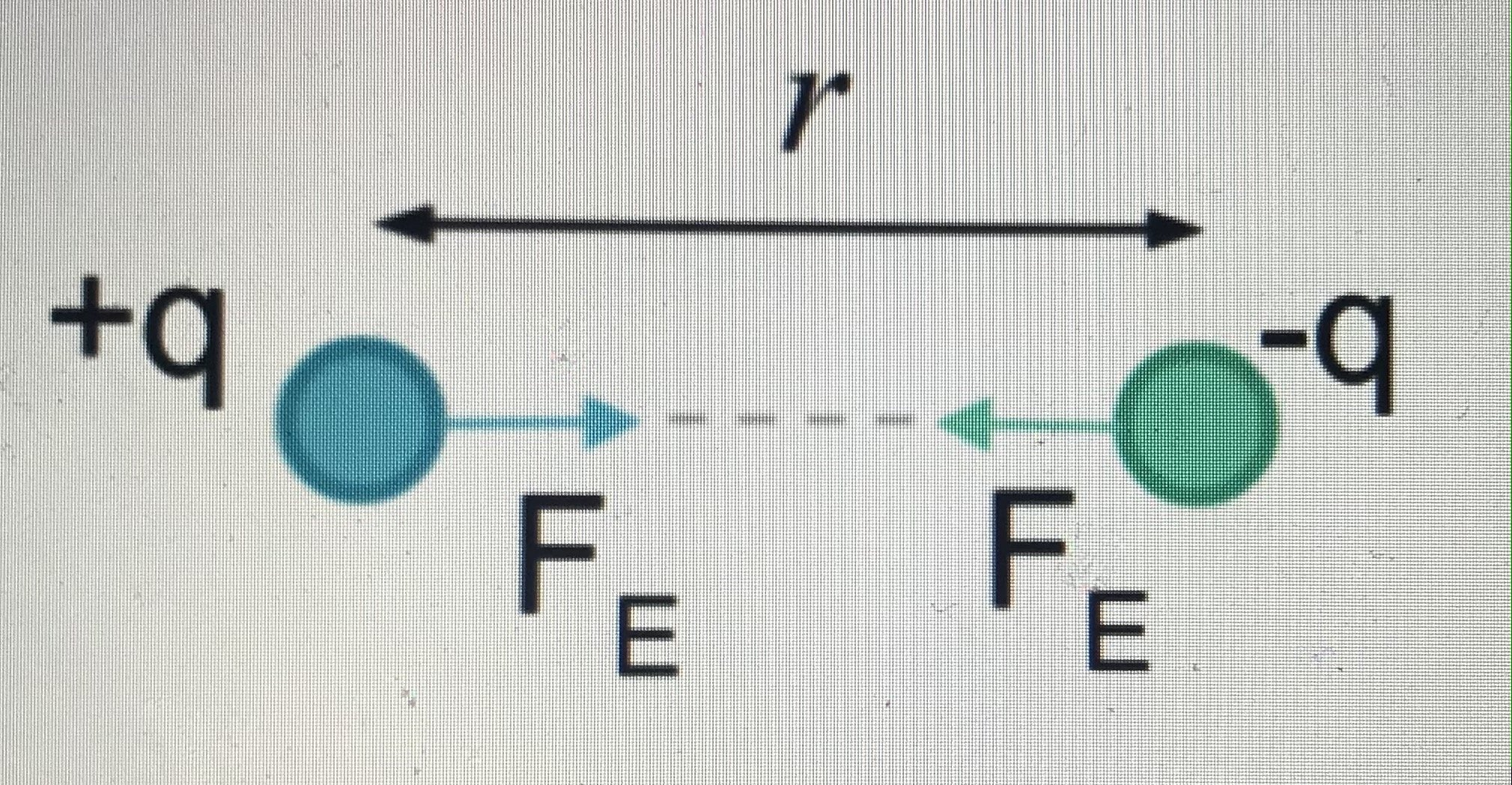
F = electric force
k = coulomb’s constant
q1q2 = charges
r = distance of separation
s = sheppard factor
The sheppard factor can have one of two values, -1 or +1. It represents whether a charge is speeding up/moving at a constant speed or slowing down. It is determined using acceleration and velocity. If acceleration and velocity are in the same direction, the charge is speeding up thus the sheppard factor is +1. If the velocity and acceleration of the charge are in opposite directions then the charge is slowing down resulting in a sheppard factor of -1.
Conventional:
Applying the sheppard factor to coulomb’s law. To show the it fits in with current understanding of how charged particles interact. It will then be applied to new mechanism.
Attraction
Let movement to the right be defined as positive (+) and movement to the left be defined as negative (-).
q1 = +q
q2 = -q
+q will be attracted to -q resulting in a change in velocity and acceleration both in the positive direction as +q speeding up towards -q. Thus the shepherd factor is equal to +1. When placed into the equation
Force = a negative value (attraction). As the force value is negative, q1 (+q) is attracted to q2 (-q). Thus using results obtained when shepherd factor is incorporated mirror expected and well understood results.
-q will be attracted to +q resulting in a change in velocity and acceleration both in the negative direction as -q speeding up towards +q. Thus the sheppard factor is equal to +1. When placed into the equation
Force = a negative value (attraction). As the force value is negative, q1 (+q) is attracted to q2 (-q). Thus using results obtained when shepherd factor is incorporated mirror expected and well understood results.
Repulsion
Let movement to the right be defined as positive (+) and movement to the left be defined as negative (-).
q1 = +q
q2 = +q
+q will be repelled by +q resulting in a change in velocity and acceleration both in the negative direction as +q is speeding away from +q. Thus the sheppard factor is equal to +1. When placed into the equation
Force = a positive value (repulsion). As the force value is positive, q1 (+q) is repelled from q2 (+q). Thus using results obtained when shepherd factor is incorporated mirror expected and well understood results.
+q will be repelled by +q resulting in a change in velocity and acceleration both in the positive direction as +q speeding away from +q. Thus the sheppard factor is equal to +1. When placed into the equation
Force = a positive value (repulsion). As the force value is positive, q1 (+q) is repelled from q2 (+q).
Thus using results obtained when shepherd factor is incorporated mirror expected and well understood results.
Thought experiment:
Assume q1 and q2 are falling from a height. q2 is an electromagnet and q1 is an iron bar. On the superior surface of q2 is a non conducting material (green) preventing q1 and q2 from ever coming into contact.
Let q2 be the electromagnet (3) and q1 be the material attracted to the electromagnet (2) eg iron and an insulator.
At the initial point, neither q1 nor q2 have a charge as they are stationary. They are then dropped. As q2 is in motion and is an electromagnet, it gains a charge. q2 having a charge results in q1 also having a charge which should bring about attraction between q1 and q2.
Assume q1 = +ve charge and q2 = -ve charge.
q1 (positive) will be attracted to q2 (negative) resulting in a change in velocity and acceleration both in the positive direction (downwards) as q1 is speeding up towards q2. Thus the sheppard factor is equal to +1. When placed into the equation
Force = a negative value (attraction). As the force value is negative, q1 is attracted to q2.
IF q2 (negative) is attracted to q1 (positive), q2 would need to move towards q1. q2 is moving the the positive direction, however if attraction occurs, that would result in it moving upwards/opposite direction to positive direction. This would require q2 to first slow down, then stop before it begins to move towards q1 which is in the opposite direction to its current direction of motion.
q2 is attracted to q1 resulting in velocity and acceleration being in OPPOSITE directions (velocity is positive while acceleration is negative) because movement of q2 towards q1 initially involves q2 slowing down and coming to a stop. As a result, the shepherd factor is equal to -1. When placed into the equation
Force = a positive value (repulsion). As the force value is positive, q2 is repelled from q1 OR at least q2 is NOT attracted to q1.
Thus in this scenario, opposite charges are both attracted and repelled. q1 will be attracted to q2 however q2 will NOT be attracted to q1.